Introduction: Why Prevention is Better Than Cure
Every organization has faced this painful moment: after
investing time, money, and effort into creating a product or service, something
small goes wrong and disrupts everything.
Imagine the below situations:
These failures don’t just cause financial losses; they damage trust, brand reputation, and customer loyalty. In many industries, such as healthcare and aviation, they can even cost lives.
The real challenge is this: most failures don’t occur because of lack of intelligence or effort. They happen because risks were not identified and addressed early enough.
This is exactly where Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) become indispensable. It is one of the most practical, systematic, and forward-looking quality tools within Lean Six Sigma.
What is FMEA?
FMEA stands for Failure Modes and Effects Analysis. It is a structured method to identify potential failure points in a product, process, or system, evaluate their effects, prioritize them, and take corrective action before they occur.
Breaking it down:
In simple terms: FMEA is a roadmap for prevention.
While Lean helps eliminate waste and Six Sigma reduces variation, FMEA focuses specifically on predicting and mitigating risk before it happens.
A Relatable Example: Road Trip FMEA
Think about preparing for a family road trip:
Each of these is a failure mode. The effects could be delays, frustration, or even accidents.
Now, imagine ranking them:
- A flat tire is serious but easily detected and fixable.
- Running out of fuel is likely if ignored.
- GPS failure could leave you lost if you don’t know the route.
By planning for these risks in advance (car checkup, spare tire, fuel tank full, maps saved offline), you reduce the chances of disaster.
That’s FMEA in everyday life. Businesses just scale it up with numbers, teams, and structured methods.
Why FMEA is a Competitive Advantage
FMEA gives organizations a competitive edge because it transforms their mindset from reactive problem-solving to proactive prevention.
Key benefits include:
At ICEQBS, we’ve seen companies save millions in hidden costs simply by embedding FMEA early in their Six Sigma journey.
The FMEA Process: A Practical Walkthrough
Conducting FMEA is not complicated if done systematically. The typical steps are:
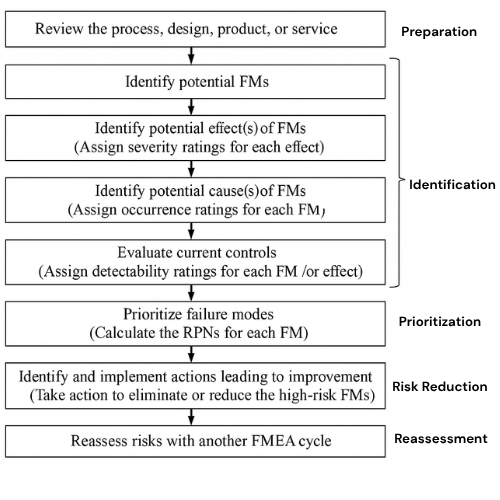
The FMEA cycle is not just a one-time exercise—it’s an ongoing journey of prevention and improvement. As processes evolve, new risks may emerge, making it important to revisit the analysis regularly.
The flowchart above demonstrates this continuous cycle: from preparation, identification, and prioritization to risk reduction and reassessment. By following this loop, organizations ensure that they are always one step ahead of potential failures.
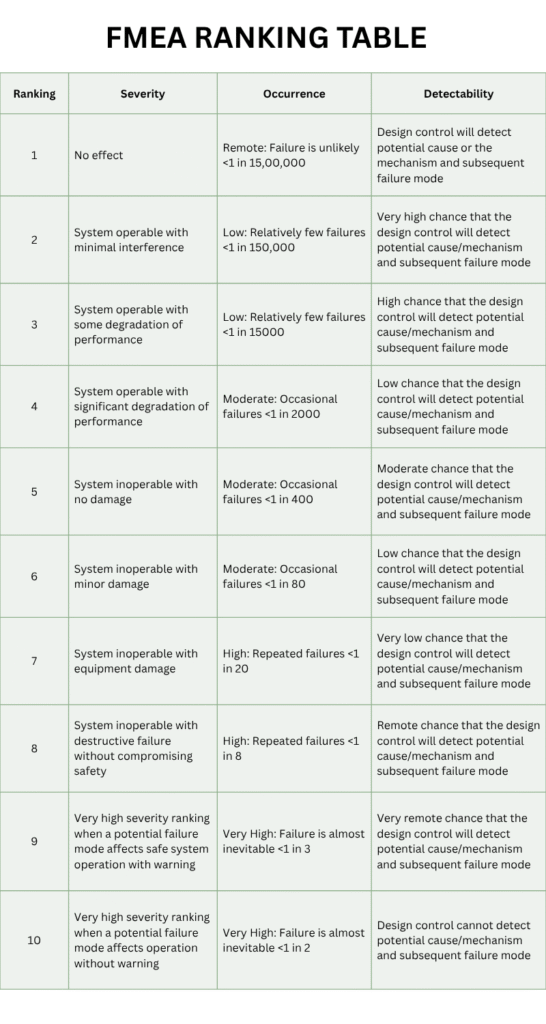
When conducting FMEA, one of the most critical steps is risk prioritization. Not all risks carry the same weight, and teams need a structured way to focus their efforts on the most urgent problems first. This is where the Risk Priority Number (RPN) table comes in.
The table allows you to compare different failure modes based on their Severity, Occurrence, and Detection ratings. By ranking risks with a numerical score, you can clearly identify which issues require immediate corrective action and which ones can be monitored over time.
To make FMEA practical and actionable, teams often rely on structured templates. An FMEA template helps organize information systematically, making it easier to identify potential failures, assess their risks, and track improvement actions. By breaking down the process into clear columns—failure modes, effects, causes, severity, occurrence, detection, RPN, and corrective actions—teams can ensure nothing is overlooked.
Below is a sample FMEA template that illustrates how organizations can document, evaluate, and prioritize risks in a structured manner:
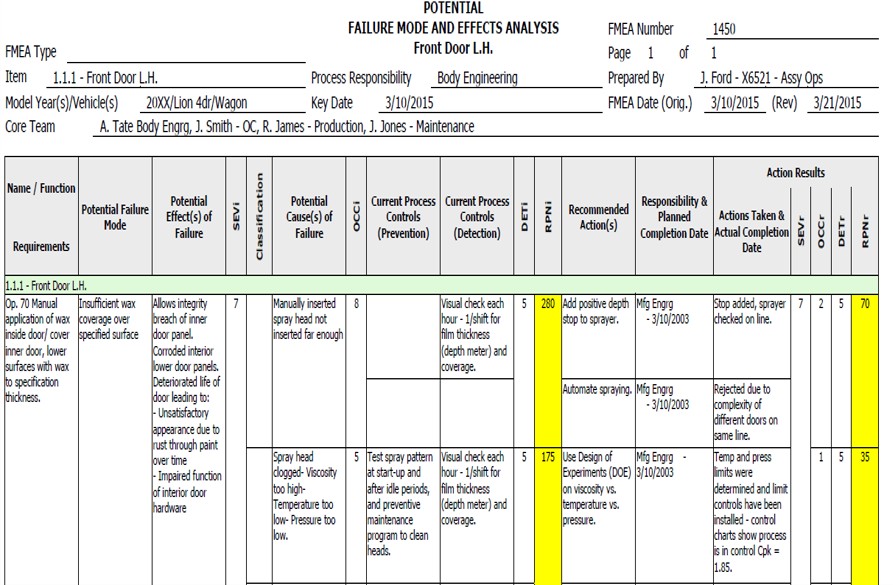
This template shows how FMEA goes beyond theory and becomes a hands-on working document for teams. While the template provides a structured framework, the real value comes from the collaborative discussions that happen when cross-functional teams work together to complete it. Every filled row represents a risk identified, understood, and controlled—bringing your organization one step closer to error-proof operations.
Final Thoughts: Building a Culture of Prevention
In today’s fast-changing business world, failure is costly, and trust is fragile. FMEA is not just a technical tool—it is a cultural shift toward prevention, responsibility, and resilience.
When done right, FMEA helps organizations deliver consistent quality, reduce risks, protect people, and strengthen their brand.
At ICEQBS, we believe adopting FMEA is not about avoiding failure—it’s about building confidence, safeguarding trust, and creating a future-ready organization.
So ask yourself:
Are you waiting for failures to happen, or are you ready to prevent them with FMEA?
Explore ICEQBS’s Lean Six Sigma training programs or consulting services today. Let’s work together to turn potential failures into lasting success through FMEA and other world-class quality tools.
![]()


